Sponsor – DOE
FIU’s Applied Research Center (ARC) is supporting the U.S. Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site in remediating uranium in F/H area seepage basins.
The F/H area seepage basins received approximately 1.8 billion gallons of acidic (pH 3.2-5.5) waste solutions contaminated with radionuclides and dissolved metals. The acidic nature of the basin waste solutions caused the mobilization of metals and radionuclides, resulting in contaminated groundwater plumes. The major constituent of concern is uranium (U). The pump-and-treat treatment system designed and built in 1997 became less effective prompting research for new remediation alternatives.
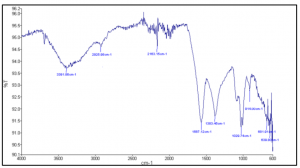
Fig 1. FTIR spectrum of Huma K which reveals aromatic functional groups
This project (i) investigates the effect of sodium silicate additions resulting in a pH increase leading to U(VI) sequestration, (ii) analyzes the soil and groundwater to verify the removal of U(VI) as well as mineralogical studies relating to the re-oxidation of a bioreduction zone, (iii) determines if the low cost Huma-K amendment can be used to facilitate uranium adsorption to control its mobility in acidic groundwater, (iv) investigates synergetic interactions between humic acid (HA) and colloidal silica that may influence the removal of uranium in the presence of SRS sediments, (v) studies the sorption of humic acid versus pH and studies the effect of HA on uranium mobility through porous media via flow-through column experiments.
The main objectives are to:
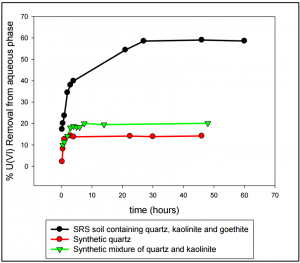
Fig 2. U (VI) removal by different mineral phases present in SRS sediments as a function of time. Results indicate that goethite plays the major role in U (VI) sequestration.
Monitor the U (VI) bioreduction after the ARCADIS demonstration at the F-Area as well as the in situ addition of a carbohydrate substrate to create reactive zones for metal and radionuclide remediation via the EARP process and evaluate for changes in sulfate concentrations and pH.
Understand the sorption and desorption of Huma-K and evaluate the effect of environmental factors that could possibly enhance desorption of Huma-K, in addition to studying the effect of Huma-K on the removal behavior of uranium.
Investigate the hypothesis that some uranium in the current treatment zone is bound to silica and study if any synergy between humic acid (HA) and silica influences the behavior of uranium.
Conduct column experiments to understand the sorption of humic acid (Huma-K) onto SRS sediments with varying pH to correlate results with HA injection tests and predict the migration and distribution of humic acid.
Benefits:
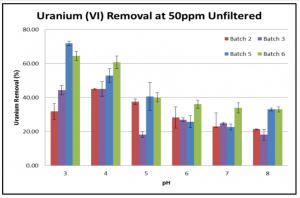
Fig 3. U (VI) removal at different pHs in the presence of 50ppm HA
Accomplishments:
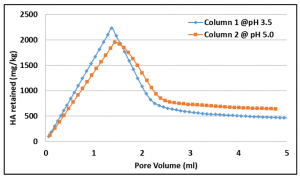
Fig 4. Retention of humic acid in the columns at different pH values
Sponsor - DOE FIU’s Applied Research Center (ARC) is supporting the U.S. Department of Energy’s Hanford Site in developing...
Sponsor - DOE FIU’s Applied Research Center (ARC) is supporting the U.S. Department of Energy’s Hanford Site in developing a...
Sponsor - DOE FIU’s Applied Research Center (ARC) is supporting the U.S. Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site in...
Sponsor - DOE This task supports US DOE EM-13 in developing plans for improving active remediation systems to improve performance...